Package overview
Title: Higher-Level Interface of ‘torch’ Package to Auto-Train Neural Networks
Whether you’re generating neural network architectures expressions or fitting/training actual models, kindling minimizes boilerplate code while preserving torch. Since this package uses torch as its backend, GPU/TPU devices also supported.
kindling also bridges the gap between torch and tidymodels. It works seamlessly with parsnip, recipes, and workflows to bring deep learning into your existing tidymodels modeling pipeline. This enables a streamlined interface for building, training, and tuning deep learning models within the familiar tidymodels ecosystem.
Main Features
- Code generation of torch expression
- Multiple architectures available: feedforward networks (MLP/DNN/FFNN) and recurrent variants (RNN, LSTM, GRU)
- Native support for titanic ML frameworks (currently supports tidymodels, mlr3 for later) workflows and pipelines
- Fine-grained control over network depth, layer sizes, and activation functions
- GPU acceleration supports via torch tensors
Supported Architectures (As of now)
- Feedforward Networks (DNN/FFNN): Classic multi-layer perceptrons for tabular data and general supervised learning
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN): Basic recurrent architecture for sequential patterns
- Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): Sophisticated recurrent networks with gating mechanisms for long-range dependencies
- Gated Recurrent Units (GRU): Streamlined alternative to LSTM with fewer parameters
Installation
You can install kindling on CRAN:
install.packages('kindling')Or install the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("pak")
pak::pak("joshuamarie/kindling")
## devtools::install_github("joshuamarie/kindling") Usage: Three Levels of Interaction
kindling is powered by R’s metaprogramming capabilities through code generation. Generated torch::nn_module() expressions power the training functions, which in turn serve as engines for tidymodels integration. This architecture gives you flexibility to work at whatever abstraction level suits your task.
library(kindling)
#>
#> Attaching package: 'kindling'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:base':
#>
#> argsBefore starting, you need to install LibTorch, the backend of PyTorch which also the backend of torch R package:
torch::install_torch()Level 1: Code Generation for torch::nn_module
At the lowest level, you can generate raw torch::nn_module code for maximum customization. Functions ending with _generator return unevaluated expressions you can inspect, modify, or execute.
Here’s how to generate a feedforward network specification:
ffnn_generator(
nn_name = "MyFFNN",
hd_neurons = c(64, 32, 16),
no_x = 10,
no_y = 1,
activations = 'relu'
)
#> torch::nn_module("MyFFNN", initialize = function ()
#> {
#> self$fc1 = torch::nn_linear(10, 64, bias = TRUE)
#> self$fc2 = torch::nn_linear(64, 32, bias = TRUE)
#> self$fc3 = torch::nn_linear(32, 16, bias = TRUE)
#> self$out = torch::nn_linear(16, 1, bias = TRUE)
#> }, forward = function (x)
#> {
#> x = self$fc1(x)
#> x = torch::nnf_relu(x)
#> x = self$fc2(x)
#> x = torch::nnf_relu(x)
#> x = self$fc3(x)
#> x = torch::nnf_relu(x)
#> x = self$out(x)
#> x
#> })This creates a three-hidden-layer network (64 - 32 - 16 neurons) that takes 10 inputs and produces 1 output. Each hidden layer uses ReLU activation, while the output layer remains “untransformed”.
Level 2: Direct Training Interface
Skip the code generation and train models directly with your data. This approach handles all the torch boilerplate when training the models internally.
Let’s classify iris species:
model = ffnn(
Species ~ .,
data = iris,
hidden_neurons = c(10, 15, 7),
activations = act_funs(relu, softshrink = args(lambd = 0.5), elu),
loss = "cross_entropy",
epochs = 100
)
model======================= Feedforward Neural Networks (MLP) ======================
-- FFNN Model Summary ----------------------------------------------------------
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
NN Model Type : FFNN n_predictors : 4
Number of Epochs : 100 n_response : 3
Hidden Layer Units : 10, 15, 7 reg. : None
Number of Hidden Layers : 3 Device : cpu
Pred. Type : classification :
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Activation function ---------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------
1st Layer {10} : relu
2nd Layer {15} : softshrink(lambd = 0.5)
3rd Layer {7} : elu
Output Activation : No act function applied
-------------------------------------------------Evaluate the prediction through predict(). The predict() method is extended for fitted models through its newdata argument.
Two kinds of predict() usage:
-
Without
newdatapredictions is the default to the parent data frame. -
With
newdatasimply pass the new data frame as the new reference.sample_iris = dplyr::slice_sample(iris, n = 10, by = Species) predict(model, newdata = sample_iris) |> (\(x) table(actual = sample_iris$Species, predicted = x))() #> predicted #> actual setosa versicolor virginica #> setosa 10 0 0 #> versicolor 0 10 0 #> virginica 0 1 9
Level 3: Conventional tidymodels Integration
Work with neural networks just like any other parsnip model. This unlocks the entire tidymodels toolkit for preprocessing, cross-validation, and model evaluation.
# library(kindling)
# library(parsnip)
# library(yardstick)
box::use(
kindling[mlp_kindling, rnn_kindling, act_funs, args],
parsnip[fit, augment],
yardstick[metrics],
mlbench[Ionosphere] # data(Ionosphere, package = "mlbench")
)
ionosphere_data = Ionosphere[, -2]
# Train a feedforward network with parsnip
mlp_kindling(
mode = "classification",
hidden_neurons = c(128, 64),
activations = act_funs(relu, softshrink = args(lambd = 0.5)),
epochs = 100
) |>
fit(Class ~ ., data = ionosphere_data) |>
augment(new_data = ionosphere_data) |>
metrics(truth = Class, estimate = .pred_class)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 accuracy binary 0.989
#> 2 kap binary 0.975
# Or try a recurrent architecture (demonstrative example with tabular data)
rnn_kindling(
mode = "classification",
hidden_neurons = c(128, 64),
activations = act_funs(relu, elu),
epochs = 100,
rnn_type = "gru"
) |>
fit(Class ~ ., data = ionosphere_data) |>
augment(new_data = ionosphere_data) |>
metrics(truth = Class, estimate = .pred_class)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 accuracy binary 0.641
#> 2 kap binary 0Hyperparameter Tuning & Resampling
The package has integration with tidymodels, so it supports hyperparameter tuning via tune with searchable parameters.
The current searchable parameters under kindling:
- Layer widths (neurons per layer)
- Network depth (number of hidden layers)
- Activation function combinations
- Output activation
- Optimizer (Type of optimization algorithm)
- Bias (choose between the presence and the absence of the bias term)
- Validation Split Proportion
- Bidirectional (boolean; only for RNN)
The searchable parameters outside from kindling, i.e. under dials package such as learn_rate() also supported.
Here’s an example:
# library(tidymodels)
box::use(
kindling[
mlp_kindling, hidden_neurons, activations, output_activation, grid_depth
],
parsnip[fit, augment],
recipes[recipe],
workflows[workflow, add_recipe, add_model],
rsample[vfold_cv],
tune[tune_grid, tune, select_best, finalize_workflow],
dials[grid_random],
yardstick[accuracy, roc_auc, metric_set, metrics]
)
mlp_tune_spec = mlp_kindling(
mode = "classification",
hidden_neurons = tune(),
activations = tune(),
output_activation = tune()
)
iris_folds = vfold_cv(iris, v = 3)
nn_wf = workflow() |>
add_recipe(recipe(Species ~ ., data = iris)) |>
add_model(mlp_tune_spec)
nn_grid_depth = grid_depth(
hidden_neurons(c(32L, 128L)),
activations(c("relu", "elu")),
output_activation(c("sigmoid", "linear")),
n_hlayer = 2,
size = 10,
type = "latin_hypercube"
)
# This is supported but limited to 1 hidden layer only
## nn_grid = grid_random(
## hidden_neurons(c(32L, 128L)),
## activations(c("relu", "elu")),
## output_activation(c("sigmoid", "linear")),
## size = 10
## )
nn_tunes = tune::tune_grid(
nn_wf,
iris_folds,
grid = nn_grid_depth
# metrics = metric_set(accuracy, roc_auc)
)
best_nn = select_best(nn_tunes)
final_nn = finalize_workflow(nn_wf, best_nn)
# Last run: 4 - 91 (relu) - 3 (sigmoid) units
final_nn_model = fit(final_nn, data = iris)
final_nn_model |>
augment(new_data = iris) |>
metrics(truth = Species, estimate = .pred_class)
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> .metric .estimator .estimate
#> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 accuracy multiclass 0.667
#> 2 kap multiclass 0.5Resampling strategies from rsample will enable robust cross-validation workflows, orchestrated through the tune and dials APIs.
Variable Importance
kindling integrates with established variable importance methods from {NeuralNetTools} and vip to interpret trained neural networks. Two primary algorithms are available:
-
Garson’s Algorithm
garson(model, bar_plot = FALSE) #> x_names y_names rel_imp #> 1 Sepal.Width y 29.04598 #> 2 Petal.Width y 27.50590 #> 3 Sepal.Length y 24.20982 #> 4 Petal.Length y 19.23830 -
Olden’s Algorithm
olden(model, bar_plot = FALSE) #> x_names y_names rel_imp #> 1 Sepal.Width y 0.56231712 #> 2 Petal.Width y -0.51113650 #> 3 Petal.Length y -0.29761552 #> 4 Sepal.Length y -0.06857191
Integration with {vip}
For users working within the tidymodels ecosystem, kindling models work seamlessly with the vip package:
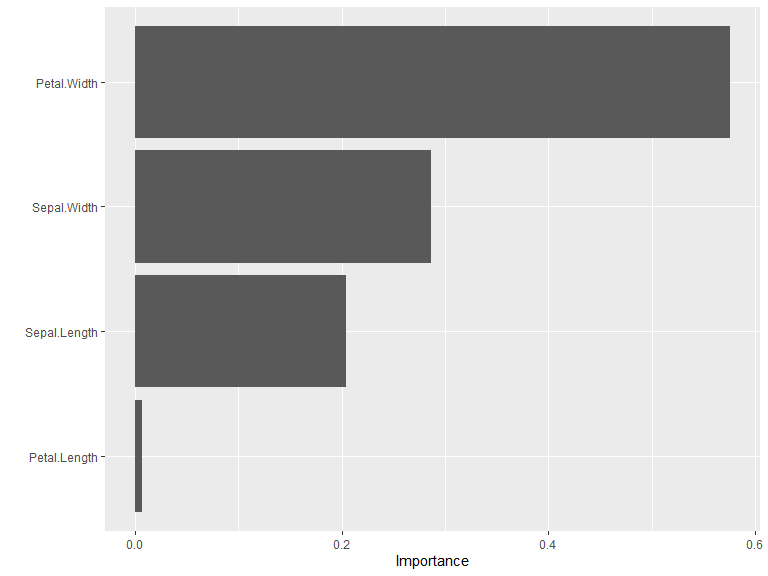
Note: Weight caching increases memory usage proportional to network size. Only enable it when you plan to compute variable importance multiple times on the same model.
References
Falbel D, Luraschi J (2023). torch: Tensors and Neural Networks with ‘GPU’ Acceleration. R package version 0.13.0, https://torch.mlverse.org, https://github.com/mlverse/torch.
Wickham H (2019). Advanced R, 2nd edition. Chapman and Hall/CRC. ISBN 978-0815384571, https://adv-r.hadley.nz/.
Goodfellow I, Bengio Y, Courville A (2016). Deep Learning. MIT Press. https://www.deeplearningbook.org/.
Code of Conduct
Please note that the kindling project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
